Surgical Anatomy
TABLE OF
CONTENTS
1 Anterior Ankle (236) 1
2 Posterior Ankle (237) 2
3 Lower Leg Posterior (251) 3
4 Lower Leg Posterior (252) 5
5 Sole of Foot 3rd Layer (257) 7
6 Anterior Foot Deep (260) 10
7 Anterior Ankle Tibiofibular Joint
(267) 12
8 Medial Ankle Joint (268) 13
9 Posterior Ankle Tibiofibular Joint
(269) 14
10 Lateral Ankle Joint (270) 15
11 Superior Tarsus (271) 16
12 Inferior Tarsus (272) 17
1
Anterior Ankle (236)
1.1
Anterior aspect of the right ankle
skeleton and superior aspect of the foot skeleton
1.2

2
Posterior Ankle (237)
2.1
Posterior aspect of the right ankle
skeleton and inferior aspect of the foot skeleton
2.2

3
Lower Leg Posterior (251)
3.1
Soleus and Plantaris muscles and the
contents of the popliteal fossa (gastrocnemius muscle removed)
3.2

3.3

4
Lower Leg Posterior (252)
4.1
Deep muscles, blood vessels, and nerves
in the posterior compartment of the right leg (soleus and Plantaris muscles
removed)
4.2
4.3 
4.4 
5
Sole of
Foot 3rd Layer (257)
5.1 Third muscular layer of the sole of the foot
5.2 Specific Remarks
5.2.1 Plantar and dorsal Interossei are arranged in their respective Intermetatarsal
spaces.
5.3 General Remarks
5.3.1 The plantar arch passes through the contents of the first
Intermetatarsal space to make a connection between the lateral plantar artery,
from the posterior tibial system, and the dorsalis pedis artery, from the anterior
tibial system. This is an important arterial anastomosis of the leg and foot
circulation.
5.4 
5.5 
6
Anterior Foot Deep (260)
6.1 Deep layer of the dorsal aspect of the foot
6.2 Specific remarks
6.2.1 The anterior tibial artery crosses anteriorly close to the skeleton
of the ankle joint to become continuous with the dorsalis pedis artery.
6.3 General remarks
6.3.1 In addition to forming an anastomosis with the plantar arch, the
dorsalis pedis artery is accessible for taking the pulse and digital
compression because of a relatively superficial position and a close
relationship to the skeleton
6.4 
6.5 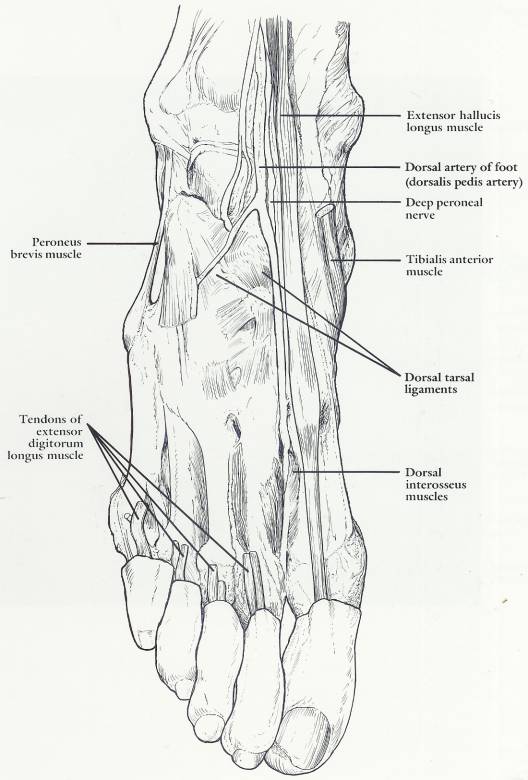
7
Anterior Ankle Tibiofibular Joint (267)
7.1 Anterior aspect of the right distal tibiofibular joint and the ankle
joint
7.2 
8
Medial Ankle Joint (268)
8.1 Medial aspect of the right ankle joint
8.2 
9
Posterior Ankle Tibiofibular Joint (269)
9.1 Posterior aspect of the right distal tibiofibular joint and the
ankle joint
9.2 
10
Lateral Ankle Joint (270)
10.1 Lateral aspect of the right ankle joint
10.2 
11
Superior Tarsus (271)
11.1 Superior aspect of the right tarsus with ligaments
11.2 Specific remarks
11.2.1
For this view the ankle joint has been
disarticulated to show the talar articular surface
11.3 
12
Inferior Tarsus (272)
12.1 Inferior aspect of the right tarsus with ligaments
12.2 















